Fast Facts: Mediterranean Diet
 Fast Facts: Mediterranean Diet www.walkjogrun.net
Fast Facts: Mediterranean Diet www.walkjogrun.net If you want to lose weight, improve your health, and strengthen your heart—without going on a traditional diet—then you should consider the Mediterranean diet.
This healthy eating plan takes the best of eating right and combines it with the flavors and traditions that you would normally find in places like Greece, Italy, and other Mediterranean locations.
Although not a traditional diet, the Mediterranean diet, or plan, may add tremendous improvements to every aspect of your health.
What Is The Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet isn’t really a diet at all. It’s a lifestyle change that focuses on healthy eating and eliminating certain foods from your diet.
By eliminating these foods, you’re left with healthier options that could lower cholesterol, improve blood pressure, reduce heart attack risk, improve brain health, and could even accelerate your weight loss.
As previously mentioned, the Mediterranean diet focuses on traditions and dietary patterns of people living in the Mediterranean, in places like Crete, Greece, Spain, Italy, Southern France, and Portugal.

What makes this diet so special?
For starters, it’s free from the deadly trans-fats that could pose a risk for your overall health, and your heart health.
And it’s free from refined oils and highly processed foods and meats.
Note: highly refined and processed foods have been linked to a number of different health issues. These foods have been shown to raise blood sugar, increase “bad” or LDL cholesterol levels, and may increase your heart attack risk. Refined and processed foods may also be contributing foods to the global obesity epidemic.
Why Would You Use The Mediterranean Diet?
To understand why you should use this diet, it’s helpful to understand how this diet came about.
Back in the 1960s, it was noticed that people live in the Mediterranean had a much lower risk for heart disease and death from coronary events, than was found in the US and other Northern European countries.
After researching different Mediterranean areas, they discovered that the style and traditions common in these countries led to a much lower risk for heart disease.
Although this was seen in the 1960s, it wasn’t until 1990 that the Mediterranean diet became wildly popular in the US and other parts of Europe.
And after years of careful study, the Mediterranean diet has been established as one of the easiest and most sustainable ways of eating that could add benefits to your health.
Even the World Health Organization (WHO) endorses this plan as a healthy and sustainable dietary pattern.
How To Include The Mediterranean Diet Into Your Life
If you would like to improve your health, lose weight, and improve the health of your brain and your heart, it’s recommended that you adopt this type of diet.

But how do you do it?
Well, it’s actually a lot easier than it sounds. It’s changing your diet to eliminate certain harmful foods and to include more of the health-boosting ones.
This plan is more of a plant-based style of eating, however, red meat can be occasionally included in this plan.
The Mediterranean plan builds meals and snacks around key foods items. Those items include:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats
- Seafood
- Eggs
- Moderate dairy intake
- And the occasional glass of red wine
One highlight of this plan that is often not talked about, but may play a huge role in the success of the plan, is the social gathering around food.
Meals in the Mediterranean are a time often spent with family and friends, which could have an emotional lift and provide you with better mental well-being.
It’s also recommended if you choose to follow this plan, to exercise regularly to add further health improvements.
What Makes The Plan So Special?
As you may or may not know, heart disease is the number one killer of both men and women around the world.
One out of every four people will suffer a heart attack this year, which accounts for over 750,000 people.
This is why, as you get older, reducing your risk for heart disease should be your number one priority.
And this plan could do just that. With a higher focus on plant-based nutrition, you could reduce your risk for heart disease by improving your blood pressure, reducing homocysteine levels, and altering your cholesterol for the better.
But how does the plan do that?
Since this plan is plant-based, with whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables as the main components to your dish, you’re able to increase the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs to keep you healthy.
Also, you’re going to increase your fiber intake, which is an important factor for not only controlling your blood pressure but for lowering cholesterol.
But it’s not just the fruits and vegetables that make this plan so special. It also has to do with the intake of healthy fats.
Healthy Fats
As you know, fat is an important part of your diet. Your body needs adequate fat in order to improve the integrity of cells, strengthen the cell membrane, and produce important hormones.
But you can’t do that without HEALTHY fats. Healthy fats, like polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats, have both been shown to improve your health and cut down on your disease risk.
And healthy fats are an integral component of the Mediterranean diet. The primary way you get healthy fats on this plan is by replacing refined oils and butter with olive oil.
Olive oil, which is high in monounsaturated fats, has been linked to improvements in cholesterol and blood pressure, as well as a boost in meal satisfaction.
That’s why it is often recommended to cook, and top foods with olive oil instead of other types of oil. However, you’re not getting healthy fats just from olive oil.
Nut and seeds also contain a fair amount of the fats that your body needs for optimal functioning.
The fats found in nuts have been linked to improvements in heart health by reducing LDL cholesterol and boosting “good” cholesterol, or your HDL cholesterol levels.
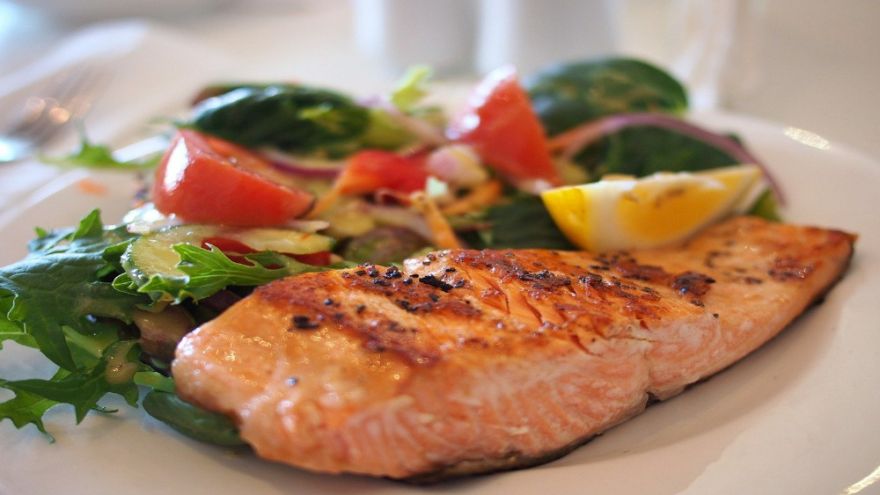
Besides nuts and olive oil, you’re also going to get a robust amount of healthy fats, called essential fats, by including more fish into your diet.
Fish, which contain the omega-3 fatty acids, are also a great source of high-quality proteins that your body needs to build lean muscle mass.

The omega-3 fats found in fatty fish, like salmon, herrings, sardines, and tuna, are very important fats that perform a number of functions in your body.
Not only do they improve heart health, but they have also been linked to improvements in brain, skin, eye, and of course, heart health.
The omega-3 fats are also important because there’s a very good chance that you are deficient in this type of fat.
Due to more people eating a Westernized diet, there is a large intake of omega-6 fatty acids and a much lower intake of omega-3 fats.
This altered ratio has been liked to poor health and premature death. However, by balancing the ratio (which should be 2:1, but currently it’s closer to 21:1), you could cut down on disease risk and add other health improvements.
Other benefits of omega-3 fats may include:
- Lower triglycerides
- Lower blood pressure
- Lower LDL cholesterol
- Increase HDL cholesterol (protective)
- Reduced blood clotting
- Lower risk for heart attack or strokes
Including more healthy fats—and less saturated and trans-fats—may boost your health, accelerate weight loss, and help you live longer.
What About Wine?
A lot of people ask about wine. As you know, people in the Mediterranean enjoy drinking wine, and it could provide some health improvements.
Red wine has been linked to improvements in health, lower cholesterol, and possibly even improved brain health.
It is recommended that you stick to one glass of wine, a couple of times a week. More than the recommended amount could pose a risk to your health.
But, if you are not a drinker, it’s recommended that you don’t start, just to get these potential health improvements, as it could be more detrimental to your health.
How To Get Started With The Mediterranean Diet
If you’re looking to get started with the Mediterranean diet, but don’t know where to start, this may help:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables—increase your intake of fruits and vegetables. Aim for 7 to 10 servings each day, and include all the colors of the rainbow.
- Opt for Whole Grains—include more whole grains into your diet. Whole-grain bread and pasta, quinoa, barley, bran, and steel-cut oats are great options for boosting your intake of whole grains. This will provide your body with the fiber it needs to stay healthy.
- Increase Healthy Fats—cut down on your intake of saturated and trans-fats, and switch to healthy fats, like olive oil and avocado oil. This will cut down on your saturated fat intake, and boost your intake of healthier mono- and polyunsaturated fats.
- Eat More Seafood—Seafood is a great source of lean proteins, as well as healthy fats. Increase your intake of fish and seafood, like sardines, crab, lobster, herring, salmon, and others.
- Reduce red meat Intake—red meat is full of saturated fat. You should replace red meat with seafood, poultry, or beans to cut down on your saturated fat intake. If you do eat red meat, keep the portions small and only indulge occasionally.
- Enjoy Dairy—dairy has been linked to weight loss and improvements in health. Enjoy Greek-style yogurt, low-fat milk, and some cheese.
- Use Spices—use spices to replace salt. Salt has been linked to high blood pressure, so reducing your intake of salt is important.
Final Thoughts On The Mediterranean Diet
Although the Mediterranean diet was first discovered in the 1960s, it wasn’t until the 1990s that this diet became very popular.
This diet, which incorporates more fruits, vegetables, nuts, and beans, is a much more sustainable way to lose weight and improve your health.
By increasing your intake of fresh and minimally processed foods, you could see improvements in the heart, brain, and overall health.
Cutting out unhealthy fats and replacing them with good fats (monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and omega-3 fats), you could put your body in a position for optimal health.
If you’re looking for a diet plan that you can do long-term, then the Mediterranean diet could be the diet for you.
References:
- Romagnolo DF, Selmin OI. Mediterranean Diet and Prevention of Chronic Disease. Nutr Today. 2017 Sep;52(5): 208-222.
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/healthy-weight/diet-reviews/mediterranean-diet/
- Agnoli C, Sieri S, Ricceri F, Giraudo MT, Masala G, Assedi M, Panico S, Mattiello A, Tumino R, Giurdanella MC, Krogh V. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and long-term changes in weight and waist circumference in the EPIC-Italy cohort. Nutr Diabetes. 2018;8:22.